Hackman's Law & Five Factor Model of Team Effectiveness
Great team conditions matter more than individual talent.
"The effectiveness of a team is determined by the sum of its members' abilities and the quality of their interactions."
♦
"The larger a group, the more process problems members encounter in carrying out their collective work …worse, the vulnerability of a group to such difficulties increases sharply as size increases."
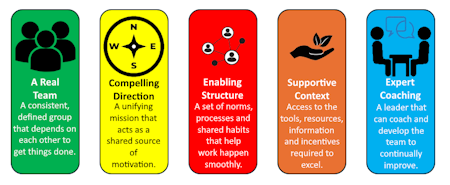
Hackman's Law states that a team's effectiveness is largely determined by how well it is set up and supported. Teams thrive when given the right conditions to succeed. Teams need more than just skilled individuals - they require a solid foundation, direction, and support to perform effectively.
The Five-Factor Model identifies essential dimensions that drive team success.
- A Real Team:
- Clear boundaries, stable membership, and interdependent work.
- Compelling Direction:
- A clear, challenging, and meaningful purpose.
- Enabling Structure:
- Well-designed roles, norms, and processes.
- Supportive Context:
- Resources, rewards, and information to empower the team.
- Expert Coaching:
- Guidance to improve teamwork and address challenges.
Teams succeed when these five factors are optimized, ensuring alignment, clarity, and coordination.
Scenario
An Agile team is working on a new product feature. They follow Scrum practices and events. However, they frequently miss Sprint Goals and deliverables are not aligning with stakeholder expectations.
Effect Observed:
Upon closer examination, it becomes clear that:
- Lack of Compelling Direction:
- The Product Owner has not provided a clear vision for the feature, leading to confusion about priorities
- Inadequate Enableing Structure:
- Team roles and responsibilities are not well-defined, causing overlap and gaps in work
- Insufficient Supportive Context:
- The team lacks access to necessary tools and resources, hindering their ability to perform tasks efficiently.
Applying Hackman's principles:
- Establish a Real Team:
- Clarify team membership and ensure everyone understands their interdependent roles.
- Define a Compelling Direction:
- The Product Owner articulates a clear vision and specific goals for the feature.
- Create an Enabling Structure:
- Assign roles based on skills and set team norms to encourage collaboration.
- Provide Supportive Context:
- Secure necessary tools, resources, and organizational support.
- Offer Expert Coaching:
- Coach the team to improve team processes and address interpersonal issues.
Outcome:
With these adjustments, the Agile team becomes focused and cohesive. They understand the objectives, collaborate effectively, and have the resources they need. This leads to improved productivity, higher-quality deliverables, and increased stakeholder satisfaction.
Summary
Hackman's research impacts Agile teams by emphasizing the foundational conditions necessary for team effectiveness. By ensuring these conditions are met, Agile teams can function more efficiently, adapt more readily to change, and achieve better outcomes.
Hackman's law emphasizes the value of clear goals, accountability, and autonomy for teams. The importance of fostering self-organizing teams.
Agile teams succeed when they are self-organizing and empowered to make decisions, enhancing collaboration, and problem-solving.